Occasional Kidney Pain
When a kidney stone forms in the right kidney, it can cause pain in the RUQ. Other symptoms of kidney stones can include: blood in the urine, which may appear red, pink, or brown. Abdominal pain from a kidney stone tends to be intermittent, usually lasting for half an hour to an hour at a time, while pain from a kidney infection is constant. Accompanying Symptoms In addition to pain, kidney problems are also sometimes accompanied by symptoms such as fever, nausea, vomiting and painful urination.
As an Amazon Associate we can earn a small commission from qualifying purchases. This commission doesn't affect products prices.
Pain typically comes and goes in waves, which is intensified by the ureters contracting as they try to push the kidney stone out.
Kidney stones are understood to cause extreme pain that usually comes and goes several times a day. Symptoms of kidney stones may not appear till the stone begins to move down the ureters.
What are the kidneys? The kidneys are two organs whose significant functions are to remove waste products and excess fluid from the body and to produce hormones that manage blood pressure, red cell production, acid policy and to influence calcium, salt, potassium and other electrolyte metabolic process.
Where are the kidneys located? The kidneys are bean-shaped organs (about 11 cm x 7 cm x 3 cm) that are found versus the back muscles in the upper abdominal area. They sit opposite each other on both the left and right side of the body; the right kidney, nevertheless, sits a bit lower than the delegated accommodate the size of the liver.
Feeling that your kidney pain comes and goes cannot be ignored. Kidney stones prevail urinary tract disorders. Kidney stones can form in your kidneys when normal substances in your urine end up being too concentrated.
When this takes place, solid product can stay in your kidney or may move down your urinary tract, ultimately losing consciousness of your body.
Symptoms of Kidney Stones
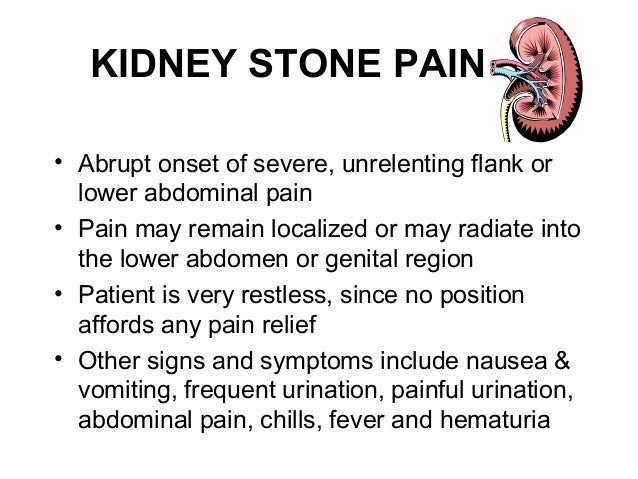
Kidney stones do not constantly cause symptoms. When they’re small, they may pass on their own without pain. However, big stones might obstruct urine circulation, which can cause a number of painful symptoms that can be severe.
This can happen when a kidney stone ends up being stuck in the ureter, which is the tube that connects your bladder to your kidneys. However, the size of the stone does not constantly represent the intensity of the pain.
In some cases, a kidney can lodge in a specific area in your kidney and cause discomfort. The pain a kidney stone causes can differ as it moves around in your kidney and down the ureter.
What are a Few of the Kidney Conditions and Illness that Cause Kidney Pain?
A number of the causes of kidney disease that lead to kidney pain (also termed flank pain) are because of gotten underlying illness that might acutely or chronically affect kidney function. Other illness are present at birth. Some people might be born with an abnormality that is genetically identified that impacts the kidneys.
Kidney pain or flank pain can be acute, fairly constant, and sharp. This is described “kidney colic.” This sort of pain is normally seen when a kidney stone or other problem obstructs the tube (ureter) that drains the kidney. Nevertheless, other procedures can cause chronic dull hurting with sometimes sharp kidney pain.
Why Does Kidney Pain Come and Go?
The location of the stone and its progress from your urinary tract can affect the type of symptoms you experience. Many people describe the feeling of kidney stones as a sharp pain on one side of their back or lower abdominal areas.
The pain frequently starts quickly and after that lingers, ending up being more extreme in time. The afflicted area can likewise spread to include the groin area and lower abdominal areas.
You may experience continuous pain, or the pain may reoccur in waves, in some cases lasting for a few minutes and then disappearing, only to resurface again about 10 minutes later on.
In many cases, the pain might last for a longer time while changing in strength. A change in the level of strength may take place as the stone relocates to a various position in your urinary tract.
Other Symptoms
In addition to feeling severe pain in your back or side below your ribs, a number of other symptoms may likewise occur with kidney stones. Among the most typical is problems with urination. This can include:
- pain while urinating
- urine that appears cloudy
- urine that smells in a different way than it generally does
- an urge to urinate more often than typical.
Blood present in the urine due to kidney stones can likewise cause urine to appear brown, pink, or red.
Difference Between Back Pain And Kidney Pain
You ought to see your doctor if you have pain with any of the following symptoms:
- queasiness
- vomiting
- chills
- a fever.
These symptoms might indicate that you have an infection.
You should also look for medical help if you have:
- pain that becomes so severe you can’t sit, stand, or rest comfortably
- blood in your urine
- difficulty urinating.
Clock Clues
If you’re unsure whether your symptoms might be associated with kidney stones, the clock might provide you with clues. Pain from kidney stones usually starts either late at night or early in the early morning.
This is due to the fact that individuals typically urinate less often at night or in the morning, and the ureter is typically restricted in the early morning.
How are Kidney Stones Detected?
Your doctor will ask you about your health history. Often medications you take may make you most likely to have a kidney stone. Examples include:
- diuretics
- calcium-based antacids
- topiramate (Topamax)
- indinavir (Crixivan).
Tests
Your doctor may confirm a diagnosis of kidney stones by buying tests. They can test your blood for the presence of excess uric acid or calcium. An accumulation of either of these can cause kidney stones to develop.
They might recommend you to gather your urine for 24 to 48 hours. A laboratory can then test it for the existence of substances that are understood to cause kidney stones to form.
Imaging Research Studies
Your doctor may use imaging research studies such as CT scans or X-rays to recognize the presence of stones in the urinary tract. An ultrasound is another noninvasive test that can check for blockages in the ureters and kidney abnormalities. Nevertheless, some stones might be so small or in such a position that they aren’t noticeable on an imaging study.
After your doctor diagnoses your kidney stones, they may give you a special strainer to use each time you urinate. You can use this to gather any stones or pieces of stones that may come out.
Collecting the stones is useful since your doctor can send them for lab analysis. Understanding what sort of kidney stones you’ve passed can help your doctor work with you to create a prepare for minimizing your risk for future kidney stones.
What is the Treatment for Kidney Pain?
Kidney pain (flank pain) treatment depends upon the underlying cause of the pain. Infections and kidney stones that cause pain are typically treated with ibuprofen, ketorolac (Toradol), acetaminophen (Tylenol and others), or sometimes with percentages of morphine (kidney stones).

However, these agents treat pain (pain relief just) and not the underlying cause(s) of pain. Nevertheless, some patients might spontaneously pass (urine sweeps the irritating kidney stone from the ureters and/or urethra) small kidney stones (usually less than about 6 mm in diameter) then be pain-free.
Infections like urinary tract infections (UTIs) and pyelonephritis typically need antibiotic treatments in addition to pain medications. If kidney stones totally obstruct a ureter or are about 6 mm in size or larger, they might need urologic surgery.
Usually, recovery time is quick (same day or a few days) if kidney stones are removed by retrograde surgical methods. Nevertheless, some severe kidney lacerations may require more substantial surgery. Recovery time for these surgical treatments varies from weeks to months.
Other underlying causes of flank pain might need similar pain management and concurrent treatments. Nevertheless, patients with known kidney problems (kidney disease) and/or renal function compromise ought to not be treated with pain medications that are either filtered (removed) through the kidneys and/or might cause additional renal damage.
Home Remedies for Kidney Stones
Phytolysinum – is a diuretic, which has a vegetable origin.
Medicinal Action Phytolysinum
The guidelines to Phytolysinum kept in mind that the drug is a diuretic, analgesic, antispasmodic, anti-inflammatory and bacteriostatic result. In the viewpoint of Phytolysinum promotes loosening and eliminating urinary stones (stones).
Release Kind and Structure
Phytolysinum offered in a soft paste in its consistency, having a green-brown color and a specific fragrant smell. 100 g of the paste consists of 67, 2 g of condensed water-alcohol mixture of the extract of medical plants: the roots of couch lawn, peel onions, fenugreek seeds, leaves of birch, goldenrod herb, parsley root, grass Bird Highlander, horsetail herb, lovage root.
In addition, the structure consists of Phytolysinum: Nipagin A Agar, orange oil, wheat starch, oil of peppermint, sage oil, pine oil, glycerin, vanillin.
Indicators Phytolysinum
Application Phytolysinum shown in the following cases:
- Infectious-inflammatory illness of the urinary tract (cystitis, pyelonephritis, chronic calculous pyelonephritis);
- Treatment of urolithiasis, particularly if there are contraindications to its surgical treatment, and avoidance of its reoccurrence.
Phytolysinum: Contraindications
The drug is contraindicated in intense glomerulonephritis and nephrosis. According to the guidelines Phytolysinum not be used in phosphate nefrourolitiaze. Pregnancy and lactation are not contraindications to Phytolysinum.
Dosing Phytolysinum
Kidney Pain Location Diagram
The drug is taken orally 3 to 4 times a day for one teaspoon, spreading out pre pasta in half a glass of warm boiled water.
Children designate Phytolysinum depending upon age – by a quarter to half a teaspoon of paste at the reception. In the opinion of Phytolysinum can be diluted in sweetened water. In this case, children are most likely to drink the resulting option.
Side Effects
Application Phytolysinum can result in allergic reactions: itching, rash. In the viewpoint of Phytolysinum very hardly ever may cause the development of queasiness, vomiting, diarrhea. When side effects of treatment should be stopped and look for medical recommendations.
Analogs Phytolysinum
Likewise with Phytolysinum action the drugs such as phytol and Urolesan. But their structure differs with the structure of Phytolysinum. For that reason, it is a good idea to take the drug, which is designated by your doctor.
Storage and Life Span
Phytolysinum ought to be kept at room temperature, out of reach of children. Expiration date – 3 years.
Passing of Kidney Stones
A lot of kidney stones will eventually leave your body by passing from the kidneys to the ureters to the bladder and out through your urine. This is the route your urine takes a trip every day. A stone going through this path can cause pain.
Passing a kidney stone can take a few days to a number of weeks. For this factor, the majority of medical professionals advise passing the stone or stones at home.
Your doctor might recommend anti-nausea or pain medications for you to take while you’re attempting to pass the stone. Drinking more water can likewise help you eliminate your urinary system, but do not exaggerate it. Consuming 2 to 3 quarts of water per day must be enough.
When Should You See Your Doctor?
Your doctor can determine the size of your stones using an imaging study. If they determine that it’s very large or you’re having signs of severe infection, it may not be safe to attempt and pass the stone at home.
Lithotripsy is a procedure that includes the use of shock waves to separate the stone into smaller sized pieces. This makes the stone much easier to pass. If this doesn’t separate the stone or the stone is in a location where lithotripsy might not work, your doctor can use more invasive methods.
This consists of inserting an unique scope called a ureteroscope into your urethra. Your doctor will advance it upward till they access the stone. Another procedure, known as percutaneous nephrolithotomy, includes making a small incision in your back to access the kidney and get rid of the stone.
You must look for emergency treatment for your kidney stone if any of the following occurs:
- You have a fever or chills, which can indicate the existence of infection.
- You stop producing urine.
- You have a history of kidney removal and have just one kidney.
- You have severe queasiness or vomiting.
- You develop confusion or severe tiredness.
- Although these symptoms are unusual with a kidney stone, they can take place.
- Even if your pain is mild, you should still seek emergency situation attention.
Types of Back Pain and Kidney Pain
Back pain is classified into neck pain, upper back pain, lower back pain or tailbone pain anatomically. It can be acute if it lasts for less than 4 weeks, sub acute if lasting for 4 to 12 weeks and chronic if present for more than 12 weeks.
Kidney pain is usually very severe and if caused due to kidney stones are known as colic which indicates its wave like occurrence as opposed to steady pain. Pain due to kidney infection is indicated by pain in flank area. All types of kidney pain are usually accompanied with fever, nausea and vomiting.
Differences in Causes
What causes back pain?
Back pain can be caused due to a number of reasons. Usually mild back pain does not require immediate medical attention. Back pain usually occurs due to inflammation. Sometimes back pain can be indicative of a serious medical condition like bone fracture, spinal fracture, multiple myeloma, osteoporosis, cancer, lumbar disc herniation, degenerative disc disease etc. Stress and dysfunctional family relationships are also known to cause back pain. During pregnancy, a majority of women experience low back pain which can be severe during the third trimester.
Causes of kidney pain
The most common cause of kidney pain is kidney stones. These stones get lodged in the ureter blocking urine flow causing severe pain which has been comparable to labor pains. Kidney pain is also caused due to pyelonephritis or kidney infection. Pain occurs due to infection and inflammation of the capsule that surrounds the kidney. Unlike back pain, both these types of kidney pain are accompanied with fever, nausea and vomiting. Other potential causes of kidney pain include cancer and bleeding inside the kidneys due to injury. Dull aching pain in kidney can be caused due to polycystic kidney disease or gradual blockage of urine flow.
Treatment and Management of Back Pain vs Kidney Pain
If back pain is not chronic, it can be managed by a hot pack and a massage; on the other hand, kidney pain is persistently acute and would need a visit to the doctor.
Back pain is managed by a number of therapies and pain medications. Even though surgery is an option, it is rarely considered unless absolutely necessary. Some of the back pain management involves use of heat therapy, massage therapy, cold compression therapy, use of muscle relaxants, physical therapy, exercises, Alexander Technique, acupuncture, electrotherapy etc. Patients commonly see a chiropractor, physical therapist or Osteopath.

Kidney pain is treated according to its cause. Treatment usually involves antibiotics and bed rest for long time. Kidney disorders can have serious implications and hence require immediate medical intervention. Removal of kidneys stones might require surgical methods if medications fail to give relief to patient.